What do you need to know about psoriasis on eyelids?
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes the rapid buildup of skin cells, resulting in the formation of thick, scaly patches. While it most commonly affects the knees, elbows, and scalp, psoriasis can also appear on the sensitive skin of the eyelids, causing various challenges in diagnosis and management. There is no known etiology of eyelid psoriasis, but genetics and immune system malfunction are thought to play a role. In addition to medications, there are numerous coping strategies and lifestyle modifications that can help manage symptoms.
Continue reading to learn more about eyelid psoriasis and what you can do to treat it.
What is Eyelid Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated condition affecting over 7.5 million people in the United States. It manifests as reddish patches of skin with painful silvery scales that burn and itch.
When the immune system is out of balance, additional skin cells are produced at a higher rate than usual. This causes the skin to thicken and become scaly (or produce plaques) in some locations. Skin cells regenerate normally over a month, but with psoriasis, this process occurs every three to four days.
Psoriasis typically affects the joints, scalp, elbows, and knees but it can also affect other parts of the body, including the eyelids and around the eyes. It can cause dryness, irritation, pain, and possibly visual loss in the eyes. When skin patches accumulate to a large enough size, they can interfere with blinking or fully closing the eyes.
Other symptoms of eyelid psoriasis may include:
- Redness and Inflammation: One of the initial signs is the appearance of red, inflammatory spots on the eyelids. These patches may cause a burning or itchy feeling.
- Scaling and Flaking: As the condition worsens, the skin on the eyelids may start to scale and flake, resembling dandruff-like particles. This can affect both the upper and lower eyelids.
- Swelling: Psoriasis on the eyelids may cause swelling, giving the eyes a puffy appearance. This can be especially distressing for people as the eyes are a prominent and sensitive facial feature.
- Cracking and Bleeding: In severe cases, the skin on the eyelids may crack and bleed, causing discomfort and making routine activities such as blinking more difficult.
What Causes Eyelid Psoriasis?
The specific causes of psoriasis are unknown, and its progression may be multifactorial. Changes in a person’s immune system may lead to the development of psoriasis. Psoriasis causes the body’s natural defenses to react improperly, resulting in the fast growth and accumulation of skin cells.
There may potentially be a hereditary component. People who have a family history of psoriasis are more likely to develop the disorder than those who do not.
Psoriasis Triggers
While immune function and genetics may play a role in the development of psoriasis, a trigger is usually required for symptoms to appear. Triggers include:
- Infections
- Stress
- Certain medications
- Sunburn
- Skin damage due to an injury, bite, or other trauma
- Environmental factors
Can Psoriasis of the Eyelids Cause Vision Loss?
Psoriasis on the eyelids is not necessarily severe, but it can be. People who acquire psoriasis around their eyes are more likely to lose their vision if they do not seek treatment as soon as possible.
What Eye Conditions Cause Vision Loss After Eyelid Psoriasis?
Several eye disorders associated with eyelid psoriasis can result in vision loss, including:
- Uveitis
- Dry eyes
- Conjunctival hyperemia
- Punctate keratitis
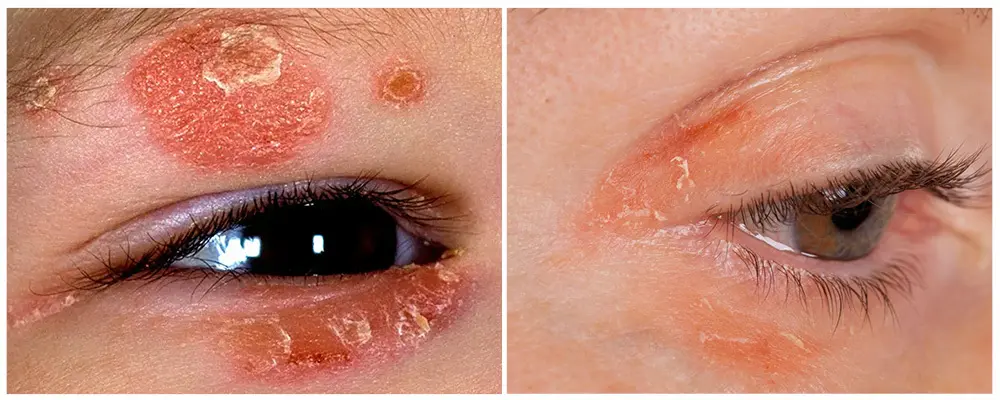
Complications of Eyelid Psoriasis
Because of its symptoms and treatments, eyelid psoriasis can lead to serious consequences. The following are some potential complications:
- Iritis and Uveitis: Inflammation of the iris and middle layer of the eye surface (the uvea).
- Conjunctivitis (pink eye): Inflammation or infection of the eyelid membranes.
- Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca (dry eyes): A lack of moisture in the eye might result in problems with vision.
- Conjunctival Hyperemia: Eye pain, sensitivity to light, copious tears, and mucus can result from redness and dilatation of blood vessels in the eye.
- Punctate Keratitis (SK): Corneal surface cells die, resulting in redness, light sensitivity, and decreased vision.
- Blepharitis: Inflammation of the eyelid.
Also read: Psoriasiform Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Approaches
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
A dermatologist diagnoses psoriasis on the eyelids after a comprehensive examination. However, due to the sensitive nature of the skin of the eyelid, it is crucial to differentiate psoriasis from other skin conditions that may present with similar symptoms, such as eczema or allergic reactions.
To confirm the diagnosis, doctors may do a skin biopsy, which involves analyzing a small piece of the afflicted skin under a microscope. A thorough medical history and physical examination are required to rule out other possible causes.
How can we Manage Eyelid Psoriasis?
If a person detects any of the following symptoms, they should consult a doctor:
- Any new or worsening psoriasis symptoms, especially on the eyelids
- Harmful effects of medicine
A doctor will evaluate a person’s condition and devise a treatment plan to control symptoms. Treatment options will be determined by the type of psoriasis, the person’s medical history, and the severity of their symptoms.
Treatment options include:
- Topical Corticosteroids: Topical corticosteroids may be effective in mild to moderate cases of psoriasis on the eyelids. These anti-inflammatory lotions and ointments assist in reducing redness and inflammation.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: When corticosteroids are not suited for long-term usage on the eyelids, topical calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus can be administered. These drugs alter the immune response and can be useful in managing symptoms.
- Emollients and Moisturizers: Keeping the skin moisturized is critical in the treatment of psoriasis. Emollients and moisturizers help relieve dry skin and keep it from cracking.
- Phototherapy: Exposing the affected eyelids to controlled doses of natural or artificial ultraviolet (UV) light may be indicated in some cases. Phototherapy can assist in reducing the fast proliferation of skin cells associated with psoriasis.
- Systemic drugs: Systemic drugs, such as oral immunosuppressants or biologics, may be administered for severe and extensive psoriasis. These treatments, however, have possible negative effects and are normally reserved for more difficult situations.
Words from Revival
Revival Research Institute is an integrated clinical research organization, and we are conducting phase III Psoriasis Clinical Trials for individuals suffering from psoriasis. Participate today!
Summary
Eyelid Psoriasis is a rare skin condition and poses great challenges because of the sensitivity of the skin in this area. Seeking immediate medical assistance and adhering to a specific treatment plan is essential for managing symptoms and increasing the quality of life of people suffering from this condition.
Without proper treatment, a person with eyelid psoriasis is more likely to develop eye diseases that might result in negative consequences such as vision loss. To avoid these consequences, a person must consult with a dermatologist as soon as they discover symptoms.




