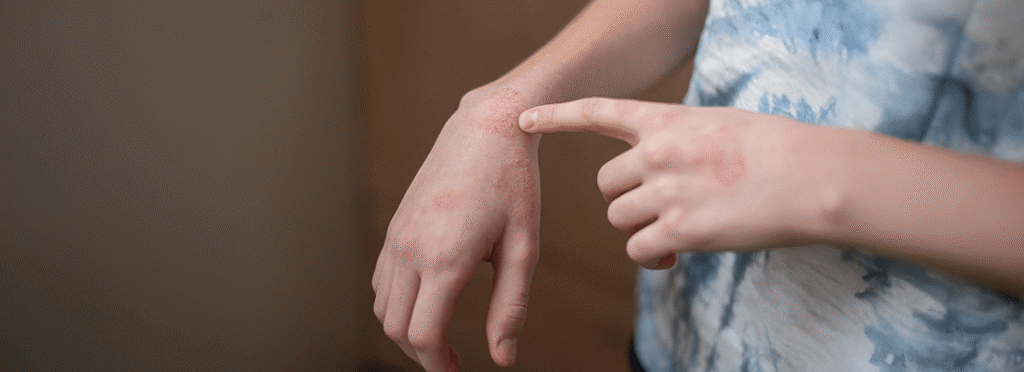
Imagine walking into an art exhibition where every canvas tells a story except one. This particular artwork looks normal from a distance, but when you come closer, the colors appear swollen, separated, and unusually inflamed. This visual disruption mirrors what happens inside the skin when someone develops spongiotic dermatitis with eosinophils. Beneath the surface, the skin layers begin separating due to fluid buildup, while eosinophils immune cells known for responding to allergic triggers rush into the tissue, creating a reaction that is often uncomfortable, itchy, and persistent.
Spongiotic dermatitis is more than a diagnosis; it is a spectrum of inflammatory skin responses. It can appear suddenly, linger for months, or become chronic depending on the triggers and the body’s immune behavior. Because these symptoms often resemble eczema, allergic reactions, fungal infections, or even autoimmune skin diseases, the condition is frequently misunderstood. Many individuals face repeated flare-ups without understanding the underlying pathology.
In this blog, we break down spongiotic dermatitis in simple yet medically accurate language. We will examine the types of subacute and chronic spongiotic dermatitis with eosinophils. We will also dive into modern diagnostics, real-world scenarios, prevalence estimates, and emerging treatments, including Atopic Dermatitis clinical trials. Whether you are a patient, caregiver, or medical professional, this guide aims to give a deeper understanding and practical insight into managing this condition effectively.
What is Spongiotic Dermatitis with Eosinophils?
It refers to a dermatological condition in which the skin develops intercellular edema (spongiosis) accompanied by eosinophil infiltration. Dermatitis with eosinophils typically involve redness, swelling, itching, and microscopic fluid accumulation between the skin cells. In pathology, this condition indicates a strong immune or allergic component. Many patients often ask, “what is this skin condition, how it happens, and why does it happen?” and the answer lies in a mixture of immune hypersensitivity, environmental triggers, and in some cases, underlying chronic inflammatory diseases.
Prevalence
The exact prevalence of this condition is not fully established because it often overlaps with eczema and allergic dermatitis. It’s chronic type is observed slightly more often in adults, while subacute spongiotic dermatitis is frequently seen in individuals with seasonal or contact allergies. Prevalence is increasing globally due to environmental allergens, pollution, and rising rates of atopic conditions, making it an important diagnosis for clinicians to recognize early.
Spongiotic dermatitis with eosinophils Causes
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Allergic reactions | One of the most common dermatitis with eosinophils causes triggered by immune hypersensitivity. |
| Contact dermatitis | Another major contributor to the list includes soaps, metals, fragrances, and chemicals. |
| Atopic predisposition | Genetic tendencies are central dermatitis with eosinophils causes in long-term sufferers. |
| Environmental irritants | Pollution and heat are emerging dermatitis with eosinophils causes in urban populations. |
| Autoimmune response | In rare instances, immune dysfunction becomes one of the primary causes. |
Signs & Symptoms Behind This Condition
| Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Intense itching | Often worsens at night; hallmark symptoms. |
| Red or scaly patches | Common during both subacute and chronic phases. |
| Oozing or crusting | Caused by fluid buildup within skin layers. |
| Burning sensations | Seen in chronic spongiotic dermatitis with eosinophils. |
| Thickened skin | Indicates long-standing inflammation. |
Subacute Spongiotic Dermatitis with Eosinophils
It represents the transitional phase between acute inflammation and chronic eczema. Many individuals experience subacute spongiotic dermatitis after exposure to allergens such as dust mites or fragrance-containing products. Physicians often see subacute spongiotic dermatitis in patients with seasonal allergy backgrounds. Because subacute dermatitis still contains eosinophil clusters, it shows an ongoing immune response. If untreated, dermatitis may progress to a chronic form requiring long-term management.
Chronic Spongiotic Dermatitis with Eosinophils
Chronic spongiotic dermatitis occurs when inflammation persists for several months. People with chronic dermatitis often experience thickened skin, repeated flare-ups, and a reduced quality of life. Many cases of chronic spongiotic dermatitis develop after years of allergic triggers or unmanaged eczema. Dermatologists diagnose chronic dermatitis with eosinophils through biopsy and clinical symptoms. Managing this chronic condition requires a combination of lifestyle changes, topical therapy, and sometimes systemic medications.
Treatment Options
| Treatment | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Topical steroids | Reduces inflammation and itching. |
| Antihistamines | Controls allergic reactions and nighttime itching. |
| Moisturizers | Helps repair the skin barrier. |
| Calcineurin inhibitors | Useful for sensitive areas (face, folds). |
| Immunotherapy or advanced biologics | Considered for severe cases. |
Atopic Dermatitis Clinical Trials: New Hope for Patients
Clinical research is evolving rapidly, and many individuals living with this condition may also qualify for Atopic Dermatitis clinical trials. These trials test innovative therapies targeting immune pathways, eosinophil activity, and chronic inflammation. Participation in Atopic Dermatitis clinical trials offers access to cutting-edge treatments not yet available in routine dermatology practice.
Modern trials focus on:
- Reducing eosinophil-driven inflammation
- Improving skin barrier recovery
- Preventing flare-up cycles
- Providing long-term remission in chronic cases
Clinical trials also empower patients to contribute to scientific progress while receiving closely supervised care.
Takeaway
Spongiotic dermatitis with eosinophils is a complex but manageable condition when properly understood and diagnosed. From dermatitis with eosinophils to developing its chronic form, each stage reveals a unique pattern of immune response. Understanding this condition, recognizing its causes, and exploring new treatments, especially through clinical trials, can help patients regain comfort and confidence. With proper medical guidance and emerging therapies, long-term relief is entirely possible.