Bringing Awareness To Men’s Health Issues During Men’s Health Month.
The Goal of Men’s Health Month:
Did you know that men die nearly five years earlier than women? One of the major reasons is that they are more hesitant to visit the doctor. Furthermore, Men’s Health Network says that certain conditions are more common in men, which patients and doctors should monitor through regular appointments.
As a result, the goal of Men’s Health Month is to raise awareness of preventable health issues and encourage early detection and treatment of disease in both men and boys. This month provides an opportunity for health care providers and individuals to encourage men and boys to seek regular medical advice and early treatment for disease and injury.
Cardiovascular Diseases in Men:
Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) is a broad term that encompasses a wide range of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels. According to the American Heart Association, over 39 million American men suffer from one or more of these conditions, and each year, just under half a million of them die from cardiovascular disease—more than cancer and diabetes combined. This Men’s Health Month, we would like to shed light on the issue of Cardiovascular Diseases in men.
In the United States, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death, and disability, lowering the quality of life for millions of people. It is critical to understand your heart to help prevent heart disease. If you have heart disease, you can live a healthier, more active life by learning about your condition and treatments and by becoming an active participant in your care by participating in Cardiology Clinical Trials.
What is a Cardiovascular Disease?
Cardiovascular disease refers to a group of conditions that affect the structure or function of the heart. They may include the following:
- Valve disease is characterized by tightness or leakage of the heart valves (structures that allow blood to flow from one chamber to another chamber or blood vessel).
- Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a problem with your heart’s blood vessels, such as blockages.
- Heart failure is characterized by a problem with the heart’s pumping and relaxing processes, resulting in fluid accumulation and shortness of breath.
- Peripheral artery disease is a constriction or blockage of the blood vessels in your arms, legs, or abdominal organs.
- Aortic disease refers to a problem with the big blood vessel that transports blood from your heart to your brain and the rest of your body, such as dilation or obstruction.
- Congenital heart disease is a cardiac condition that is present at birth and can damage various sections of the heart.
- Pericardial disease refers to problems with the heart’s lining, such as pericarditis and pericardial effusion.
- Cerebrovascular disease is a constriction or blockage of the blood arteries that transport blood to the brain.
- Arrhythmia is a problem with your heart’s electrical conduction system that causes abnormal heart rhythms or heart rates.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blockage in the veins and capillaries that return blood from the brain and body to the heart.
Why is Heart Disease Primarily a Male Issue?
Although the mortality rate for cardiovascular events or conditions has decreased significantly in the last 20 years, heart disease remains the leading cause of death in men.
Overall, men are more likely than women to develop heart disease; one in every seven men and one in every eleven women will die from heart disease. The causes of Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) numbers in men are thought to be a variety of factors.
Men have more difficult jobs and deal with stress differently than women. They are less likely to follow a healthy diet, are more likely to be overweight than women, and may be less aware of their symptoms and well-being. This Men’s Health Month, prioritize your heart health and schedule an appointment with a physician near you.
What are the Symptoms of Cardiovascular diseases?
Because cardiovascular disease often has no symptoms, you may not realize you have it until you have a heart attack or stroke. In men, the most common symptoms of a heart attack are severe chest pain, pain in the left arm or jaw, and difficulty breathing. Stroke symptoms include facial muscle weakness and/or arm weakness, as well as difficulty speaking or understanding.
Depending on the type of cardiovascular disease you have, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Chest pain, tightness, pressure, or discomfort
- Arm and/or leg pain, weakness, or numbness
- Arm, neck, shoulder, jaw, or back pain or discomfort
- Breathing difficulty
- Excessive fatigue during activity Abnormal heart rhythm
- Feeling dizzy, lightheaded, or fainting
- General ailment or fatigue
- Hands, legs, and feet swell
How are Cardiovascular Diseases Diagnosed?
To diagnose cardiovascular disease, your doctor will review your medical and family history, run some tests (such as blood tests), and examine you (such as measuring your blood pressure) to see if you have any known risk factors.
To assess your risk of cardiovascular disease, your doctor may use an online risk assessment tool such as the cardiovascular disease risk calculator.
Your doctor may order additional tests based on the results of your initial tests, examination, and risk assessment.
- Blood tests look for cholesterol and certain proteins in the blood, which are indicators of cardiovascular health.
- The electrical activity in your heart is recorded by an electrocardiogram (ECG).
- Wearable gadgets that track your heart rhythm and rates are used in ambulatory monitoring.
- Sound waves are used to create an image of your heartbeat and blood flow during an echocardiogram.
- Cardiac CT creates images of your heart and blood vessels using X-rays.
- Cardiac MRI creates images of your heart using magnets and radio waves.
- Stress tests employ a variety of methods to stress the heart in a controlled manner (exercise or drugs) to assess how your heart responds via EKGs and/or pictures.
- A catheter (a thin, hollow tube) is used to detect pressure and blood flow in your heart during cardiac catheterization.
What are the Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors?
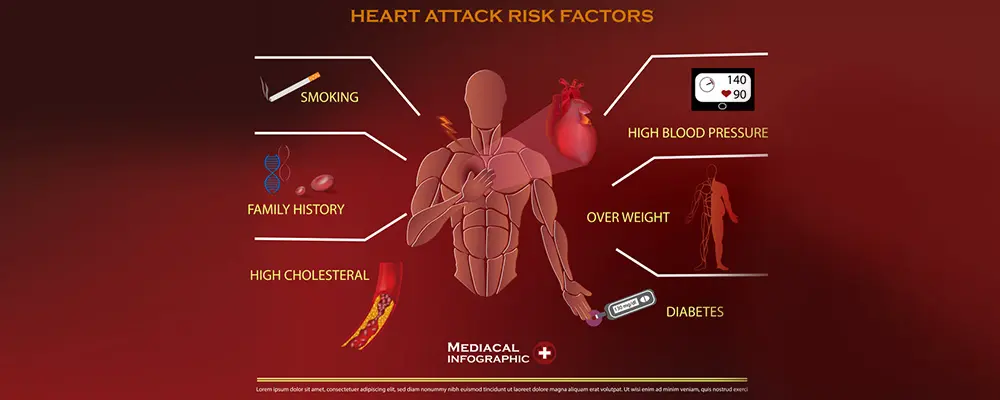
The following are some of the risk factors for heart disease:
- Age: As you become older, you’re more likely to have damaged and restricted arteries, as well as a weakened or thicker heart muscle.
- History of the Family: A family history of heart disease raises your risk of coronary artery disease, especially if one of your parents was diagnosed at a young age.
- Smoking: Nicotine constricts blood arteries, while carbon monoxide damages their inner lining, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis. Smokers are at a higher risk of heart attacks than nonsmokers.
- Poor dietary habits: A high-fat, high-salt, high-sugar, and high-cholesterol diet can all contribute to the development of heart disease.
- High blood pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure can cause your arteries to stiffen and thicken, narrowing the veins from which blood flows.
- High cholesterol: Plaque development and atherosclerosis are both increased by high cholesterol levels in the blood.
- Diabetes: Diabetes increases your chances of acquiring heart disease. Obesity and high blood pressure are common risk factors for both illnesses.
- Obesity: Other heart disease risk factors are often worsened by excess weight.
- Physical inactivity: Lack of exercise is linked to many types of heart disease, as well as some of the disease’s other risk factors.
- Stress: Unresolved stress can harm your arteries and exacerbate other heart disease risk factors.
- Dental health: Brushing and flossing your teeth and gums regularly, as well as having regular dental checkups, are essential. Germs can enter your bloodstream and go to your heart, producing endocarditis, if your teeth and gums aren’t healthy.
How can I Lower my Chances of Developing Heart Disease?
To reduce your chances of developing heart disease this Men’s Health Month, you should do the following:
- Understand your blood pressure. Uncontrolled blood pressure leads to heart diseases. Because high blood pressure has no symptoms, it is critical to have your blood pressure checked regularly.
- Diabetes increases your risk of heart disease. Consult with your doctor that you get test for diabetes.
- Stop smoking. Don’t start smoking if you don’t already.
- Consult your doctor about having your cholesterol and triglyceride levels checked.
- Prepare nutritious food. Obesity and being overweight increase your risk of heart disease.
- Limit your alcohol consumption to as much as one drink per day.
- Reduce your stress level and learn healthy stress coping strategies.
What are the Complications of Cardiovascular Diseases?
The following are some of the complications of cardiac disease:
- Heart failure: Heart failure happens when your cardiac is unable to pump enough blood to meet your body’s needs. It is one of the most prevalent complications of heart disease. Many types of heart illness, including heart defects, circulatory disease, valvular heart disease, heart infections, and cardiomyopathy, can lead to heart failure.
- Heart attack: A heart attack is cause by a blood clot obstructing blood flow through a blood vessel that feeds the heart, potentially injuring or killing a section of the heart muscle. A heart attack can be caused by atherosclerosis.
- Stroke: The same risk factors that cause cardiovascular disease can cause an ischemic stroke, which occurs when the arteries leading to your brain become restricted or clogged, allowing too little blood to reach your brain. A stroke is a medical emergency because brain tissue starts to die within only a few minutes.
- Aneurysm: An aneurysm is a bulging in the wall of your artery that can occur anywhere in your body and is a dangerous issue. You may have life-threatening internal bleeding if an aneurysm rupture.
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD): A condition that affects the arteries in the Peripheral artery disease occurs when blood flow to your extremities — generally your legs — is insufficient. This results in symptoms, the most common of which is leg pain during walking (claudication). Atherosclerosis is one of the reasons for peripheral artery disease.
- Sudden cardiac arrest: Sudden cardiac arrest is the loss of heart function, respiration, and consciousness that occurs suddenly and unexpectedly, usually as a result of an arrhythmia. A medical emergency is sudden cardiac arrest. It can lead to abrupt cardiac death if not addressed right away.
When Should You Seek Expert Advice About Your Cardiovascular Health?

If you have any symptoms of chest pain, worsening breathlessness with exertion, or palpitations, get yourself evaluated.
A thorough clinical examination and non-invasive diagnostics (such as ultrasound and CT scanning) can help confirm or refute the presence of significant heart artery disease. Even if you don’t have any symptoms, knowing your risk of future events can help you avoid the potentially fatal consequences of a heart attack. Schedule an appointment with your doctor this Men’s Health Month and keep track of your heart health.
Will Cardiac Rehabilitation Improve my Treatment?
Cardiac rehabilitation aids in the recovery of your heart’s strength. It provides further assistance in modifying your lifestyle. It entails nutritional counseling as well as exercise that is closely monitored.
If you need heart surgery, your healthcare professional may recommend cardiac rehab. If you’ve had a heart attack or a stroke, you might be eligible for treatment.
And If you’re having problems sticking to your cardiovascular disease treatment plan on your own, cardiac rehabilitation can be a viable option. Check with your doctor to see whether you’re eligible for a hospital-based program. They might recommend a different, safe, and healthy treatment plan for you.
Bottomline:
Cardiovascular illnesses impact the heart and blood vessels of the body. Cardiovascular disease can lead to heart attacks or strokes if not treated properly. To address cardiovascular disease, you might make lifestyle modifications or use drugs. Early detection can aid in effective therapy.
Men have a reputation for avoiding doctors and ignoring unusual symptoms. This could explain why women live longer lives. Don’t let your health suffer as a result of your laziness.
Make appointments with your doctor for yearly checkups and keep them. Your doctor can help you keep track of your weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels. Obesity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol levels are all risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes, medications, or other treatments to help you control your weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol.
These are just a few ways for men to stay healthy as they age, and Men’s Health Month is a great time to commit to better health! Make the effort for yourself – and your family.
Help the men you know live a healthier, happier life! Stay Heart Healthy this Men’s Health Month and prioritize your health.




