Introduction
What is your understanding of Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis? Have you ever had either of the two skin conditions? If you have, you must agree with the classic hallmarks of the two conditions (Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis). Red, purple, dry, itchy, scaly, and inflamed skin are some of the mirror symptoms between the two conditions causing them to be misdiagnosed. In addition, exploring viable treatment options for synonymous conditions can be difficult. Enrolling in dermatology clinical trials might help eliminate hindrances to potential new treatment options.
Stick around to learn more about Seborrheic Dermatitis and Psoriasis: What’s the difference? Can seborrheic dermatitis be mistaken for psoriasis? What triggers seborrheic dermatitis? And how one can prepare to combat the conditions.
Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis: The Distinction & Similarities
One of the most important distinctions between seborrheic dermatitis vs psoriasis is that psoriasis occurs as an autoimmune response of the body, triggering inflammation and abnormal skin production. Want to learn more about psoriasis? Here’s an interesting and in-depth piece on psoriasis.
While the 2 conditions are the results of an inflammatory response presenting as a rash, the question arises – can seborrheic dermatitis be mistaken for psoriasis? In either case, understanding the distinguishing characteristics is important to gain the right diagnosis and work on managing the condition.
| Characteristics | Seborrheic Dermatitis | Psoriasis |
|---|---|---|
| Affected Areas | Scalp, face, ears, chest & areas with many oil glands | Scalp, elbows, knees, lower back & nails |
| Redness and Inflammation | Mild to moderate redness & inflammation | Often more pronounced redness & inflammation |
| Flaky, Itchy Skin | White or yellowish scales, often accompanied by itching | Silver or whitish scales, with intense itching |
| Distribution of Lesions | Commonly in areas with more oil glands (oily areas) | Can appear in various areas, not necessarily oily ones |
| Severity | Typically milder in severity | Can range from mild to severe |
| Scalp Involvement | Common; causes dandruff | Common; leads to thick, scaly patches on the scalp |
The Different Types of Psoriasis
There are different types of psoriasis, such as plaque, flexural, guttate, inverse, pustular (common in females and chain smokers), and erythrodermic. Each of them owns a particular set of characteristics and triggers.
With every subtype, comes a particular set of symptoms:
- Stable plaque psoriasis
– The most common type of psoriasis causes dry, itchy, raised skin plaques. - Flexural psoriasis
– Typically found on the flexor surfaces such as the groin, natal cleft, and sub-mammary area. - Guttate psoriasis
– This condition is characterized by “raindrop-like” plaques over the trunk, following 2 weeks post-strep throat infection. It is commonly found in children and young adults. - Erythrodermic and pustular psoriasis
– The 2 types of psoriasis often occur together, and are collectively called “Von Zumbusch psoriasis”. Moreover; it is considered the most severe form of psoriasis, capable of inducing a dermatological emergency with clinical features such as malaise, fever, and circulatory disturbance.
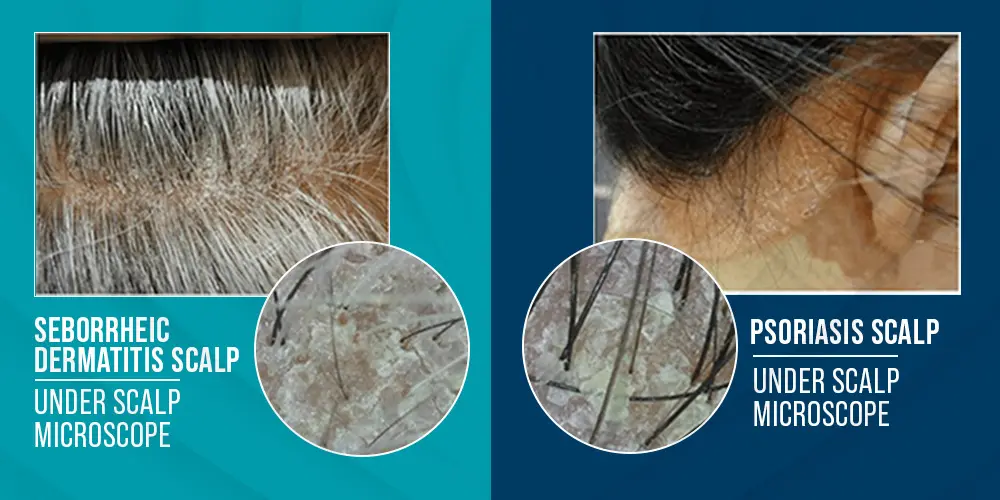
Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis
The concomitant occurrence of Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis is a rare sight. However, understanding “Seborrheic Dermatitis and Psoriasis: what’s the difference?” may be beneficial to you.
Seborrheic dermatitis, a subtype of dermatitis classified under the “Endogenous” domain is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the skin, commonly seen in Parkinson’s and HIV. The pathogenesis behind the manifestation of the disease is attributed to a strong immune response, caused by the overgrowth of the fungus “Malassezia furfur”.
Psoriasis, on the other hand, is more than just a skin condition and can take a toll on one’s mental and physical well-being if left untreated.
Also read: Comprehensive Guide to Living with Papular Eczema
Clinical Manifestations of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a T-cell-mediated skin disorder and is a consequence of a triad including increased cellular turnover, and inflammation alongside angiogenesis. The typical clinical features indicative of psoriasis are:
- Erythematous, salmon-colored plaques enclosed with silver-white scales. Sometimes associated with the “Auspitz sign” (pin-point bleeding at the site where the scale wears off due to a thin epidermis).
- Nail bed changes (nail pitting, crumbling, detachment from the nail bed) in 50% of the cases.
- Koebnerization (new plaque formation at the sites of repeated trauma).
While the clinical observation of the site of the rash is essential before you can infer any diagnosis, a major understanding of the specific site involvement in seborrheic dermatitis vs psoriasis can help to ease the task.
- A rash commonly involving the “extensor” surfaces is thought of as psoriasis.
- A rash commonly involving the scalp, face, and trunk is thought of as seborrheic dermatitis.
Clinical Presentations of Seborrheic Dermatitis
Listed below are some of the commonly encountered clinical presentations of seborrheic dermatitis with age:
- In adults, an uninflamed form of seborrhoeic dermatitis affects the scalp and presents as asymptomatic, diffuse bran-like scaly patches, or mild pruritis.
- In infants aged between 3 months to 6 months, a characteristic “Cradle Cap” such as thick crusting of the scalp is common.
- In other instances, a generalized seborrheic dermatitis (Leiner Diseases) with accompanying symptoms such as diarrhea and failure to thrive might occur.
Factors Influencing Psoriasis
While psoriasis itself is non-transmissible (it is not contagious), it may run in families. In addition, psoriasis is one such condition that proves that resting genetic diseases may be triggered in response to the environment. Factors that may be triggering include:
- Stress
- Infections
- Medications
- Weather
- Lifestyle adaptations
Cause of Seborrheic Dermatitis
The etiological cause of seborrheic dermatitis is unclear. However, several factors associated with the incidence of the condition are:
- Hormonal fluctuations
- Fungal (yeast) infections
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Neurogenic factors (Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, facial nerve injury)
- The proliferation of Malassezia (yeast) appears to be the major culprit
In addition to the factors stated above, understanding what triggers seborrheic dermatitis is equally important to better manage flare-ups.
What Triggers Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Triggering factors of the condition range from stress and hormonal changes to the use of certain detergents or medications. Other factors responsible for seborrheic dermatitis flareups are:
- Stress
- Recovery from a stressful life event
- Hormonal fluctuations
- Illness
- Use of harsh detergents, solvents, chemicals, and soaps
- Weather changes
- Certain medications (psoralen, interferon, and lithium)
What Triggers Psoriasis?
Stress
- Injury to the skin
- Use of medications like lithium and quinidine
- Infection, including strep throat, bronchitis, and tonsillitis
Can Seborrheic Dermatitis be mistaken for Psoriasis?
Can seborrheic dermatitis be mistaken for psoriasis? The answer to it is vague. However, referring to specialists specialized in Dermatology can help distinguish between the two conditions.
The two conditions often mimic each other because of the overlap of symptoms such as red skin patches with flakes on the scalp and back. Hence the answer to the question, “Can Seborrheic Dermatitis be mistaken for Psoriasis?” is YES.
Treatment Options Available
The goal of treatment is aimed at slowing down the proliferation of skin cells and relieving itching and skin dryness which is a major concern in many skin conditions. The treatment options available for psoriasis are:
- Steroid creams
- Moisturizing creams and lotions
- Coal tar (indicated for treating scalp psoriasis)
- Vitamin D-based cream or ointment
- Retinoid creams
- Calcineurin inhibitors
- Anthralin
Available treatment options for managing seborrheic dermatitis are:
- Keratolytics (salicylic acid, lactic acid)
- Topical antifungal ointments/creams (Ketoconazole)
- Topical corticosteroids
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors (an alternative to corticosteroids, as they have fewer side effects)
Also Read: Spongiotic Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis: The Takeaway
Psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis are two common skin conditions that can be easily confused with one another. It is because they share similar clinical features such as redness and dry scaly patches. Therefore; understanding seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis: what’s the difference? might be challenging but not impossible. To help overcome the difficulties, Revival Research Institute is conducting dermatology clinical trials investigating potential new treatment options for psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, and other skin conditions.




