They say a picture is worth a thousand words, but a rash can leave you speechless when it comes to skin conditions. Imagine waking up one morning to find your skin covered in small, raised bumps. Panic might set in, but understanding the culprit behind these bumps can bring some peace of mind. So, let’s dive into the world of papular rash and explore their causes, symptoms, and how to manage them effectively.
What Is a Papular Rash?
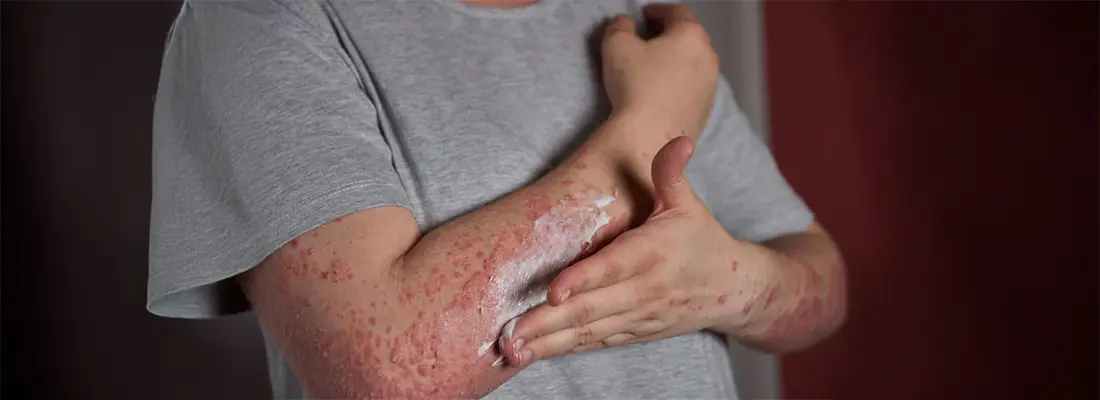
A papular rash or raised skin bumps are characterized by small, raised, solid bumps on the skin, each usually less than one centimeter in diameter. Unlike other rashes that might appear flat or fluid-filled, papules are firm and can vary in color from red to brown or flesh-toned. This type of rash can occur anywhere on the body and can be itchy or non-itchy, depending on the underlying cause.
The Unexpected Causes of Papular Rash
Unraveling the mystery of what causes this condition can sometimes feel like detective work. There are numerous potential triggers, ranging from infections to allergic reactions and even systemic diseases.
- Infections: Viral infections like chickenpox, measles, and shingles are common culprits. Bacterial infections, such as those caused by staphylococcus or streptococcus, can also lead to such a condition.
- Allergic Reactions: Contact with allergens like poison ivy, certain foods, or medications can cause the immune system to react.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions such as lupus and dermatomyositis can cause chronic raised skin bumps as part of the body’s immune response.
- Heat Rash: Also known as miliaria, heat rash occurs when sweat ducts become blocked, leading to irritation and the formation of papules.
Symptoms of Papular Rash
Recognizing these rashes involves noting their distinct characteristics. Here are the key symptoms to look out for:
- Small, firm, raised bumps on the skin
- Red, brown, or flesh-colored papules
- Possible itching or tenderness
- Occurrence in clusters or scattered patches
While these symptoms can be uncomfortable, understanding them helps in identifying the rash’s nature and seeking appropriate treatment.
Papular Rash vs. Maculopapular Rash: Spot the Difference
It’s easy to confuse a papular rash with a maculopapular rash, but there are distinct differences. Here’s a quick comparison to help differentiate between the two:
| Feature | Popular Rash | Maculopapular Rash |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Small, raised, firm bumps (papules) | Flat or slightly raised, red spots (macules) |
| Texture | Solid and firm | Mixed flat and raised areas |
| Common Causes | Infections, allergies, autoimmune diseases | Viral infections, drug reactions |
| Itchiness | Varies (can be itchy or non-itchy) | Often itchy |
| Size of Lesions | Less than 1 cm in diameter | Variable size, usually larger |
Understanding these differences can help in diagnosing and treating the rash effectively.
Precautions: Keep Calm and Take Care
When dealing with this condition, taking necessary precautions can prevent further irritation and aid in recovery. Here are some creative and practical tips:
- Stay Cool: Avoid overheating, as sweat can aggravate the rash. Wear loose, breathable clothing and stay in air-conditioned environments if possible.
- Hydrate and Moisturize: Keeping your skin hydrated is essential. Drink plenty of water and use gentle, fragrance-free moisturizers to soothe the skin.
- Avoid Scratching: While it may be tempting, scratching can lead to infections. Keep your nails short and consider using anti-itch creams to reduce discomfort.
- Identify and Avoid Triggers: If you suspect an allergen or irritant is causing the rash, try to identify and avoid it. This might involve changing skincare products or dietary habits.
Papular Rash Differential Diagnosis: A Critical Step
Accurately diagnosing these rashes involves considering other conditions that might present similarly. This process is known as differential diagnosis and can include:
- Acne: Papules can be a feature of acne, especially on the face, back, and chest.
- Psoriasis: Characterized by red, scaly patches that can include papules.
- Scabies: Caused by mites, leading to intense itching and rashes, particularly at night.
Consulting a dermatologist is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Potential Treatment Protocols: The Road to Recovery
When it comes to treating this condition, the approach depends on the underlying cause. Here are some potential treatment protocols:
- Topical Treatments: Corticosteroid creams can reduce inflammation and itching. Antibacterial or antifungal creams may be necessary if an infection is present.
- Oral Medications: For severe or widespread rashes, oral antihistamines, antibiotics, or antifungals might be prescribed.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Managing stress, avoiding known triggers, and maintaining good skin hygiene can prevent flare-ups.
Dermatology clinical trials are also exploring innovative treatments and therapies for various skin conditions, offering hope for more effective solutions.
Prevalence of Papular Rashes
Papular rashes are a common dermatological concern worldwide, affecting people of all ages and backgrounds. Their prevalence varies based on the underlying cause. For instance, viral infections like chickenpox are more common in children, while autoimmune-related rashes can occur in adults. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), skin diseases, including those presenting as papular rashes, affect millions globally, highlighting the need for continued research and awareness.
Conclusion: Embrace the Journey to Healthy Skin
Dealing with this ailment can be a perplexing and uncomfortable experience, but understanding its nature, causes, and treatment options can make the journey smoother. Remember, the key is to stay informed, take necessary precautions, and seek professional advice when needed. With the right approach, you can manage and overcome the challenges posed by these rashes, paving the way to healthier, happier skin.
In conclusion, whether you’re facing a mild rash, or a more persistent condition, knowledge and proactive care are your best allies. So, keep calm, stay informed, and embrace the journey to a clear and healthy skin.