Introduction
Intrinsic eczema lacks widespread recognition because of its comparatively more recognized counterpart, extrinsic eczema. It is also known as non-allergic eczema. While extrinsic eczema is associated with allergies, this type of eczema operates differently at a biological level.
Although it does share some commonalities with extrinsic eczema, its root cause lies within the internal triggers of the immune system and genetics. Determining whether you have intrinsic or extrinsic eczema involves identifying specific symptoms and underlying causes.
This article discusses what signs to be more attentive towards and how this kind of eczema can be treated effectively.
For a deeper understanding of the causes, symptoms, and treatments of intrinsic eczema, continue reading.
What is Intrinsic Eczema?
Atopic dermatitis is known to be associated with elevated levels of immunoglobulin E (IgE). Individuals with atopic dermatitis also exhibit other atopic conditions such as allergies, resulting in an oversensitive immune response. However, in people afflicted with this kind of eczema, IgE levels remain within the normal range, whereas other atopic conditions are absent.
Also read: Is Eczema An Autoimmune Disease?
Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic Eczema
The primary difference between the two subtypes of atopic dermatitis lies in the origin of symptoms. To differentiate, intrinsic is set off by allergens, whereas extrinsic eczema is not.
To have a better understanding of the differences, some of them are mentioned below:
| Intrinsic Eczema | Extrinsic Eczema |
|---|---|
| NOT triggered by allergens | Triggered by allergens |
| Usually begins in adulthood | Begins in childhood |
| Not common & mostly occurs in women rather than men | It has higher prevalence |
| Symptoms tend to be moderate | Symptoms tend to be more severe |
| Normal range of IgE levels | Elevated levels of IgE |
| Not associated with allergies such as food allergies, asthma, and allergic rhinitis | It is associated with food allergies, asthma, and allergic rhinitis |
| Not prone to skin infections | Prone to skin infections |
| Roughly 20% of the eczema cases are intrinsic | However, 80% of the cases account for extrinsic eczema |
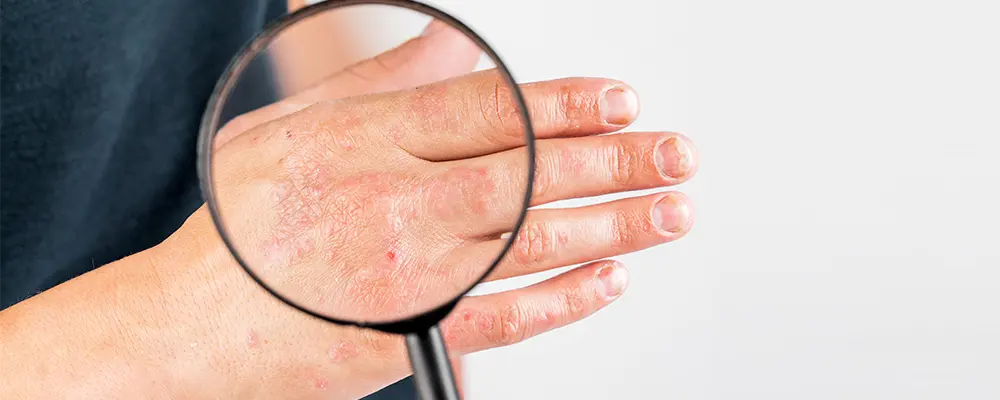
What are the Symptoms of Intrinsic Eczema?
Some of the major symptoms of this kind of eczema may include:
- Extreme itching
- Tender and painful skin
- Disturbance in sleeping pattern
- Dry skin
- Discoloration of skin
- Thickening and hardening of the skin
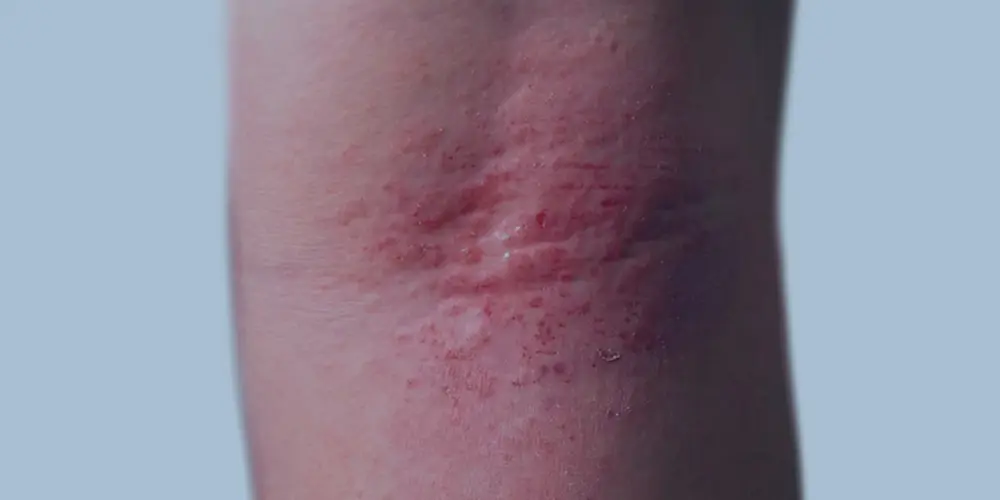
- Rashes that commonly occur on the face, neck, hands and in the bends of elbow
Also read: Flexural eczema: Symptoms, Causes and Treatments
What are the Causes of Intrinsic Eczema?
The exact cause of this kind of eczema still remains unknown. However, some of the potential causes are listed below:
- Combination of genetic mutations
- An overactive immune system
- Environmental factors that induce skin dryness
- Triggers like humidity, chilly weather, and stress
- May manifest without a discernible cause
How can Intrinsic Eczema be Diagnosed?
To diagnose this skin condition, a physical examination is required. Your physicians will evaluate your symptoms and carefully examine the affected area to determine whether it is eczema or any other condition. Family history needs to be considered as well. To significantly distinguish between the different subtypes of eczema, your healthcare provider may want to test your IgE levels. These tests play a crucial role in determining the specific subtype.
While in some cases, a skin biopsy might be suggested, which involves removing a tissue sample for lab examination. Moreover, the measurement of IgE levels through a blood test is more commonly utilized.
How can Intrinsic Eczema be Treated?
It is advised to seek prompt medical attention for persistent issues. While there is no cure for this condition presently, various treatments can readily help manage the condition. Several measures can be taken to alleviate these symptoms such as:
- Managing dry skin by regularly moisturizing with hypoallergic products, avoiding hot showers and using a humidifier for added moisture.
- Controlling itching by using gentle cleansers, applying anti-itch creams, and considering cool compress for instant relief from itching.
- Preventing triggers and avoiding flare-ups by wearing breathable, loose-fitting clothing and opting for hypoallergenic laundry products.
- Avoiding secondary infections or complications by practicing good hygiene, treating any cuts or wounds to minimize the risk of infections.
The treatment options for this skin condition may include a combination of the following therapies, depending on the severity of symptoms:
Moisturizers:
Individuals with this condition usually have dry skin that results in itching, rashes, and thickened skin patches. Hence, moisturizers can potentially help manage dry skin.
Topical Treatments:
These are creams or ointments directly applied to the skin, to eradicate inflammation.
Also read: Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors & Treating Atopic Dermatitis
Oral Medication:
These are taken in the form of pills or capsules, orally to manage and lower the symptoms by suppressing the immune system.
Phototherapy:
By utilizing UV light waves, phototherapy suppresses the body’s immune response. It is beneficial particularly in those cases that are unresponsive to other treatments.
Participate in Atopic Dermatitis Clinical Trials
What are Home Remedies for Intrinsic Eczema?
The following home remedies may help lessen the symptoms:
- Cool compresses: Apply cool compresses to affected areas to alleviate inflammation associated with the condition.
- Use of coconut oil or tea tree oil: Use moisturizing properties of coconut oil or tea tree oil known for its anti-inflammatory properties to nourish and calm the affected skin.
- Aloe vera gel: Soothe irritated skin with aloe vera gel, known for its anti-inflammatory and healing properties.
- Lukewarm bath: Take lukewarm baths to hydrate and soothe the skin and avoid hot water that can further escalate the condition.
Outlook
Understanding the root cause of atopic dermatitis is crucial for tailored treatment. While the exact cause remains unknown, recognizing symptoms is key to finding effective solutions to alleviate the condition. While intrinsic eczema exhibits symptoms like extrinsic eczema, their origins are distinct.
Living with eczema can be challenging as it can negatively impact one’s sense of self-worth. However, there are numerous Clinical Research Organizations in the US evaluating novel potential therapies that could potentially improve this condition, offering hope for an improved sense of self-esteem.