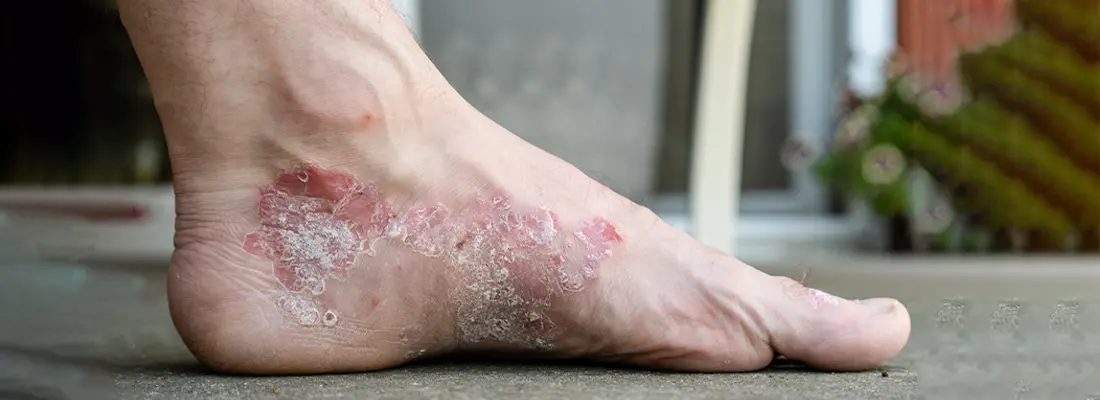
Imagine the discomfort of cracked, inflamed skin on your feet that aches with every step, or the embarrassment of red, scaly patches that no amount of ointment seems to soothe. For those living with psoriasis on feet, this isn’t just an occasional inconvenience, it’s a daily challenge that affects mobility, self-esteem, and quality of life. While traditional treatments have provided some relief, new research and clinical trials into psoriasis on feet is exploring innovative therapies that promise better outcomes and longer-lasting remission for those affected. With scientists now investigating targeted therapies and immune-modulating treatments specifically for psoriasis on feet, there is new hope on the horizon for effective, tailored solutions to this chronic condition.
What is Psoriasis on Feet?
Psoriasis on feet is a specific manifestation of psoriasis, an autoimmune condition that causes rapid skin cell turnover, leading to red, scaly patches. Although psoriasis can affect nearly any part of the body, when it appears on the feet, it often takes on a unique set of characteristics. These lesions tend to be thick, hard, and sometimes crack, making walking or even standing painful.
Psoriasis on feet can come in various forms, including:
- Plaque psoriasis (with dry, scaly patches)
- Localized pustular psoriasis also known as palmoplantar pustular psoriasis – (with pus-filled blisters)
- Erythrodermic psoriasis (in severe cases, leading to widespread redness and peeling)
Living with Psoriasis on Feet
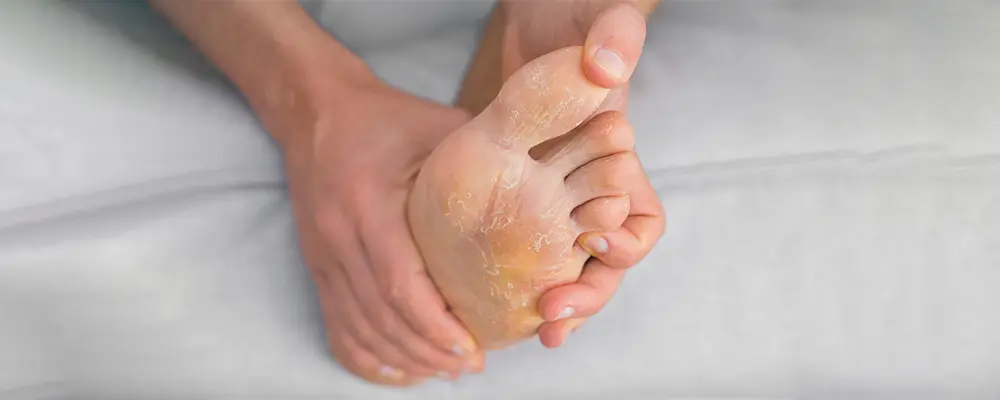
In the United States, about 2% of the population is affected by psoriasis, with many experiencing symptoms on sensitive areas like the feet. Living with psoriasis feet can be difficult, especially for those who lead an active lifestyle or work in roles that require extensive standing or movement. The physical discomfort of cracked, sore feet can lead to limited mobility and affect emotional well-being. The condition may also cause individuals to feel self-conscious, leading to social isolation or distress, especially in social situations where they may want to hide the affected area.
Managing psoriasis feet effectively often involves a combination of medical treatments and lifestyle adjustments. Footwear that minimizes pressure, for instance, can alleviate pain, while maintaining proper hygiene and moisturizing routines can prevent flare-ups. Patients can also benefit from support groups or counseling, as living with psoriasis can take a toll on mental health.
Causes and Symptoms of Psoriasis Feet
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder, meaning the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing rapid cell turnover. While the exact cause remains unknown, it’s understood that genetic and environmental factors both play a role.
Common Triggers for Psoriasis Feet
- Genetics
- Infections
- Stress
- Skin Injuries
- Cold Weather
- Smoking and Alcohol
Recognizable Symptoms of Psoriasis Feet
- Red, Scaly Patches: This is a hallmark sign of plaque psoriasis, often appearing on the soles of the feet.
- Itching and Burning: Many individuals experience severe itching and a burning sensation.
- Thickened Skin: In some cases, the skin on the feet becomes unusually thick, hard, and prone to cracking.
- Pus-filled Blisters: Common in pustular psoriasis, where white pustules form on top of inflamed skin.
- Pain and Cracks: Painful fissures are common, making it difficult to walk or stand.
Prognosis of Psoriasis on the Feet
Psoriasis is a chronic condition, meaning there’s currently no cure. However, the severity of psoriasis in feet varies significantly among patients. Some may experience only mild symptoms, while others face painful, recurrent flare-ups that interfere with daily life. With effective management, individuals can reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
As Dr. Ali Moiin, M.D, a board-certified dermatologist at Revival Research Institute, states:
“With new treatments available, patients today have better control over psoriasis than ever before. However, maintaining remission requires commitment and consistency with prescribed treatments and lifestyle changes.”
Diagnosis of Psoriasis Feet
Diagnosing psoriasis on the feet generally involves a clinical examination by a dermatologist, who assesses the physical appearance of the skin lesions. The healthcare provider may also take a small sample of skin (biopsy) to differentiate psoriasis from other skin conditions like eczema or athlete’s foot.
Sometimes, especially when patients are present with pustular or erythrodermic psoriasis, additional tests may be necessary to rule out infections or other autoimmune disorders. For a complete diagnosis, doctors consider personal and family medical history, symptom duration, and any recent infections or injuries that might have triggered the condition.
Treatment for Psoriasis Feet
Treating psoriasis on the feet can be challenging due to the skin’s thickness and exposure to pressure from walking and standing. Effective management often requires a combination of topical medications, systemic treatments, and lifestyle modifications.
| Corticosteroids | Topical corticosteroids help reduce inflammation and redness, offering relief from discomfort. |
|---|---|
| Vitamin D Analogues | These help slow skin cell growth and are commonly used in combination with corticosteroids. |
| Moisturizers | Regular use of thick emollients can help prevent cracks and reduce dryness. |
Systemic Treatments
| Biologics | Targeted therapies that focus on specific immune system components. Biologics have been effective in managing psoriasis and reducing flare-ups. |
|---|---|
| Oral Medications | Drugs like methotrexate and cyclosporine may be prescribed, though they come with side effects and require monitoring. |
| Phototherapy | This treatment involves controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, which can help slow cell growth and reduce inflammation. |
Lifestyle Modifications
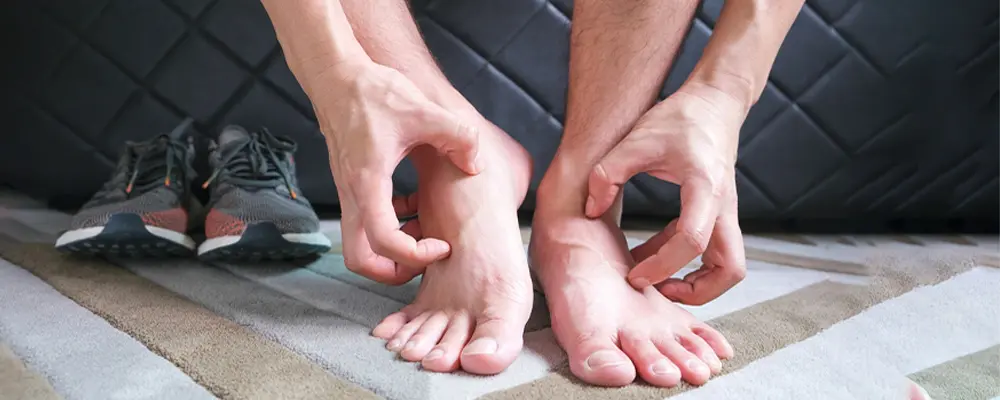

| Avoiding Known Triggers | Identifying and avoiding triggers such as certain foods, stress, or cold weather can be helpful. |
|---|---|
| Footwear Considerations | Shoes that provide ample cushioning and avoid excessive pressure on the affected areas are essential for comfort. |
| Stress Management | Techniques like mindfulness, meditation, or gentle exercise can reduce stress, a known trigger for psoriasis flare-ups. |
Conclusion
Living with psoriasis on feet presents a unique set of challenges, but advances in treatments have made it more manageable than ever before. Through a combination of topical treatments, systemic therapies, and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can achieve significant relief. While there is no cure for psoriasis feet, commitment to a treatment plan and proactive management can help keep symptoms in check, allowing individuals to maintain an active, fulfilling lifestyle.
For those experiencing symptoms of psoriasis feet, consulting a dermatologist for a tailored treatment approach is highly recommended. Early intervention can make a substantial difference, providing patients with the tools to manage flare-ups and achieve a better quality of life.