Updated on August 7, 2023
What Is Follicular Eczema?
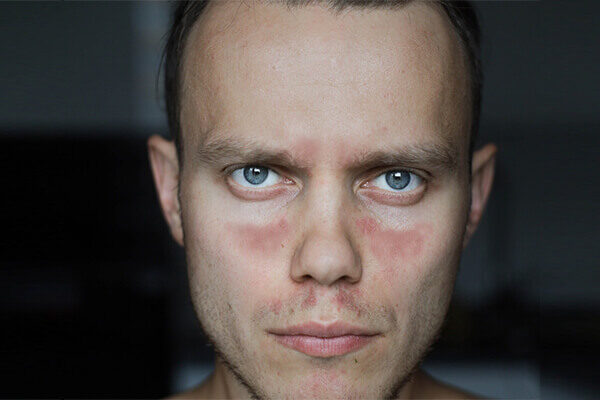
Follicular eczema is a common skin condition or type of eczema that affects the hair follicles. This condition resembles atopic dermatitis (atopic eczema) in its symptoms and appearance, as both can cause itching, redness, and discomfort. It usually appears on the upper arms, thighs, buttocks, or cheeks as small, rough, red, or flesh-colored bumps on the skin. The condition is characterized by the accumulation of keratin, a protein that forms the outer layer of the skin, which clogs the hair follicles and causes these bumps to form. People with darker skin tones are more prone to this type of eczema.
It is a non-contagious skin condition. It is more noticeable in the winter or when the skin is dry. The exact cause of follicular eczema is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. While there is no cure for follicular eczema, there are several treatments that can help manage the symptoms and improve the appearance of the affected skin.
What Are The Symptoms Of Follicular Eczema?
Symptoms seen are almost similar to those of other types of eczema or dermatitis. However, its location is what distinguishes it apart. Skin irritation mostly occurs in hairy areas of the body, including the chest, abdomen, back, upper arms, groin, and thighs.
Symptoms may include:
- Small bumps: The condition is distinguished by the presence of small, rough bumps on the skin. These bumps are frequently red or flesh-colored and can resemble goosebumps or acne most commonly found on the upper arms, thighs, buttocks, or cheeks.
- Rough or dry skin: The affected skin may feel rough and dry to the touch. It may also have a sandpaper-like texture.
- Itching: Follicular eczema can cause mild to severe itching. The desire to scratch the affected areas may be strong, but scratching will irritate the skin and worsen the condition.
- Inflammation: The skin around the bumps may appear inflamed, with redness and mild swelling.
- Increased visibility: When the skin is dry or cold, the bumps may become more visible. They may also become more visible after showering or bathing.
“Did you know Papular Eczema is the type of eczema in which small itchy rashes appear on the body in the form of bumps called Papule?”
What Causes Follicular Eczema?
The exact cause of follicular eczema is unknown. It is a skin condition caused by a genetic predisposition that causes the immune system to react to certain environmental triggers, allergens, or irritants. Typical triggers include:
- Exhaust from cars
- Dust
- Mold Infection
- Certain foods
- Laundry detergents and soaps
- Rough fabric such as wool
- Cosmetics, perfumes, lotions, sprays, and lotions
Follicular eczema, in particular, may be caused by a decrease in skin barrier function. Because of a lack of certain skin barrier proteins, this is common in people with eczema. Bacteria and other microbes can enter the skin and cause inflammation when the barrier function is compromised. Scratching itchy skin can cause cracks and bleeding, increasing the likelihood of bacterial or fungal infection. These skin infections can cause folliculitis (inflammation of the hair follicles), resulting in follicular eczema symptoms.
How Can We Diagnose Follicular Eczema?
A doctor will diagnose follicular eczema during a physical examination. This condition is distinct because it only affects individual hairs. However, testing is required to figure out what’s causing the symptoms in the first place.
Based on what one was exposed to when symptoms appeared, one may be able to determine the cause of irritant contact dermatitis. Allergen contact dermatitis is more difficult to diagnose because symptoms can appear days after being exposed to the allergen.
To determine contact allergies, a patch test is commonly performed. A variety of suspected allergens are applied to small patches on an individual’s exposed back by a doctor (an allergist or dermatologist). The patches are removed after 48 hours to check for skin reactions. The doctor will check the skin again a few days later for any delayed reactions.
A prick or scratch test, in which a small amount of a specific allergen is placed into the skin, is also used for allergy testing. If anyone has an allergy, they should notice a reaction within 30 minutes.
Follicular Eczema and Atopic Dermatitis:
Follicular eczema and atopic dermatitis have several similarities, but also some differences. Both conditions cause discomfort due to skin inflammation and itching. Follicular eczema is distinguished by the appearance of small, itchy bumps around hair follicles, most commonly on the arms, legs, and buttocks, whereas atopic dermatitis is distinguished by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, most commonly on the elbows and knees.
Scratching can aggravate the red or flesh-colored bumps of follicular eczema, similar to how atopic dermatitis’ persistent itch can cause skin thickening and scaling over time. Both of these conditions are associated with immune system dysfunction and can be aggravated by factors such as friction, sweating, and irritants. While their treatment approaches overlap, involving topical corticosteroids, moisturizers, and trigger avoidance, a precise diagnosis by a dermatologist is essential to determine the most effective management plan for each condition. Various Clinical Research Organizations in Michigan are conducting paid Atopic Dermatitis Clinical trials investigating potential treatment options.
What Is The Treatment Of Follicular Eczema?
There is currently no cure for follicular eczema, but we can learn how to reduce flare-ups and treat their symptoms by working with a doctor and dermatologist.
Learning how to care for your skin is one of the first steps. It is important to learn the best ways to bathe and hydrate your skin to keep it healthy.
Bathing
The first step in treating follicular eczema is to provide adequate skin care. To avoid worsening dry skin, bathe or shower in warm (not hot) water. People might also want to try oatmeal baths and bleach baths, which can help reduce inflammation, restore skin barrier function, and eliminate harmful bacteria. Before attempting a bleach bath, one must consult with a doctor for medical advice, and be sure to follow their instructions for diluting the bleach correctly. Shorter baths are better for the skin, and gentle skin cleansers free of dyes and fragrances are less likely to irritate the skin and exacerbate eczema.
Moisturizing
If anyone has eczema, they must keep their skin moisturized. Thicker moisturizers, such as shea butter, petroleum jelly, and certain lotions, can be used to treat affected skin. Use a fragrance-free moisturizer to avoid introducing additional allergens or irritants to the skin. After bathing, when the skin is warm and moist, it is the best time to use a moisturizer.
Steroid Creams
Topical corticosteroids, such as hydrocortisone, are also used for the treatment of eczema. However, steroids are typically only effective for short periods. Consult your doctor about this option. Some steroids are available without a prescription, while others require one. Newer nonsteroidal creams can be used to reduce the use of steroids on the skin.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy may be beneficial for people suffering from severe eczema. It is a treatment in which a clinician exposes one’s skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet light. This treatment is usually effective for all skin tones and shades.
Also read: All You Need To Know: What Causes Eczema Flare-ups?
Outlook
Follicular eczema is an inflammation of the hair follicles that causes a dotted red rash. Follicular eczema can develop due to genetic factors, problems with the skin barrier, or immune system issues. Treatment for follicular eczema includes avoiding triggers, using topical medications, and moisturizing the skin regularly. A healthcare professional can assist a person in locating the best treatments for their skin.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are responses to some commonly asked questions about follicular eczema.
Are eczema and folliculitis similar?
While folliculitis is not a type of follicular eczema, eczema can heighten the risk of folliculitis.
What triggers follicular eczema?
Genetic factors, issues with the skin barrier, and immune system problems can contribute to the development of follicular eczema.
Can follicular eczema be contagious?
Follicular eczema is not a contagious condition.